SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) , oft geschrieben als SMART , ist ein Überwachungssystem, das in Computerfestplatten ( HDDs ), Solid-State-Laufwerken ( SSDs ) und eMMC-Laufwerken enthalten ist.
Seine Hauptfunktion besteht darin, verschiedene Indikatoren der Laufwerkszuverlässigkeit zu erkennen und zu melden, um bevorstehende Hardwareausfälle vorherzusehen. In diesem Beitrag zeigen wir Ihnen, wie Sie den SMART Failure Predict Status von Laufwerken in Command Prompt , PowerShell und Performance Monitor überprüfen .
Überprüfen Sie den SMART Failure Predict Status(Check SMART Failure Predict Status) von Laufwerken(Drives) in Windows 11/10
Sie müssen als Administrator angemeldet sein, um diese Option zu verwenden.
Wenn sich eine Festplatte ( HDD ) nach dem Leerlauf derzeit in einem ausgeschalteten Zustand befindet, wird sie in diesem Bericht nicht angezeigt. In diesem Bericht werden nur Laufwerke angezeigt, die derzeit eingeschaltet sind und ausgeführt werden.
1] Um den SMART Failure Predict Status von Laufwerken(Drives) in der Eingabeaufforderung(Command Prompt) zu überprüfen , gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
- Drücken Sie die Windows key + R , um das Dialogfeld „Ausführen“ aufzurufen.
- Geben Sie im Dialogfeld Ausführen cmd ein und drücken Sie dann die Eingabetaste , um die (Enter)Eingabeaufforderung(Command Prompt) zu öffnen .
- Geben Sie im Eingabeaufforderungsfenster den folgenden Befehl ein und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste(Enter) .
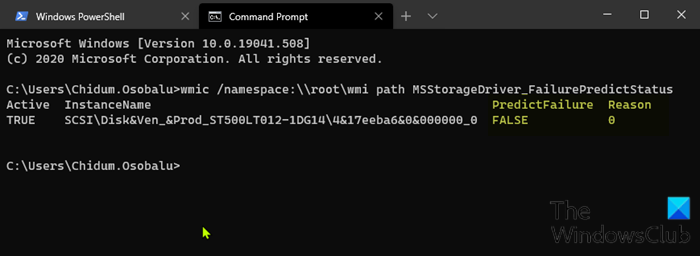
wmic /namespace:\\root\wmi path MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictStatus
- Wenn der PredictFailure eines Laufwerks als FALSE angezeigt wird , wurden keine Probleme mit dem Laufwerk gefunden.
- Wenn der PredictFailure eines Laufwerks als TRUE angezeigt wird , suchen Sie in der Tabelle am Ende dieses Beitrags nach der Grundnummer für die ID, um herauszufinden, was dies bedeutet .(Reason number)
2] Um den SMART Failure Predict Status of Drives in PowerShell zu überprüfen , gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
- Drücken Sie die Windows key + Xum das Power User-Menü(open Power User Menu) zu öffnen .
- Drücken Sie dann i auf der Tastatur, um PowerShell zu starten .
- Geben Sie in der PowerShell -Konsole den folgenden Befehl ein oder kopieren Sie ihn und fügen Sie ihn ein und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste(Enter) .
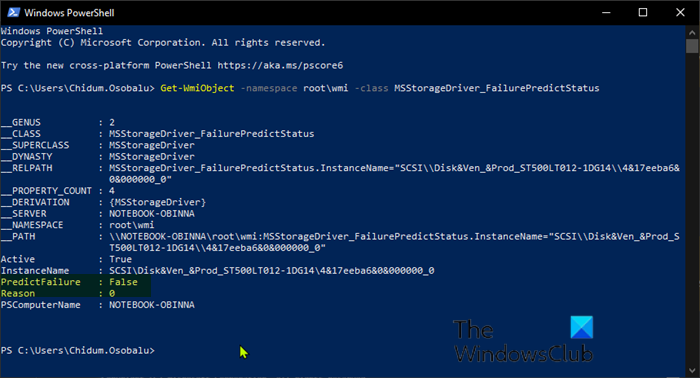
Get-WmiObject -namespace root\wmi -class MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictStatus
- Wenn der PredictFailure eines Laufwerks als FALSE angezeigt wird , wurden keine Probleme mit dem Laufwerk gefunden.
- Wenn der PredictFailure eines Laufwerks als TRUE angezeigt wird , suchen Sie in der Tabelle am Ende dieses Beitrags nach der Grundnummer für die ID, um herauszufinden, was dies bedeutet .(Reason number)
Verwandt(Related) : SMART Failure Predicted on Hard Disk error.
3] Um den SMART Failure Predict Status of Drives in Performance Monitor zu überprüfen , gehen Sie wie folgt vor:
- Rufen Sie das Dialogfeld Ausführen auf.
- Geben Sie im Dialogfeld ein
perfmonund drücken Sie die Eingabetaste, um den Systemmonitor zu öffnen(open Performance Monitor) . - Erweitern Sie Data Collector Sets, erweitern Sie System im linken Bereich von Performance Monitor .
- Klicken Sie mit der rechten Maustaste oder halten Sie Systemdiagnose gedrückt(System Diagnostics) und klicken/tippen Sie auf Start .
Dieser Bericht beginnt nun mit der Datenerfassung für 60 Sekunden. Es kann bis zu weiteren 60 Sekunden dauern, bis der Bericht erstellt wird.
- Wenn die Generierung des Systemdiagnoseberichts(System Diagnostics report) abgeschlossen ist, erweitern Sie Berichte(Reports) > System > Systemdiagnose(System Diagnostics) im linken Bereich des Systemmonitors(Performance Monitor) .
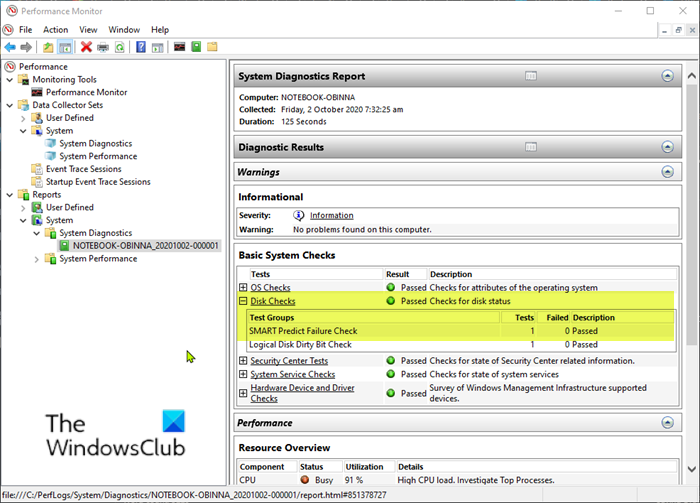
- Klicken/tippen Sie unter Systemdiagnose auf einen (System Diagnostics)Bericht(report) , der an diesem Datum und zu dieser Uhrzeit erstellt (gesammelt) wurde, und erweitern Sie Festplattenprüfungen(Disk Checks) im Abschnitt Grundlegende Systemprüfungen(Basic System Checks) unter Warnungen(Warnings) .
Wenn SMART Predict Failure Check FALSE mit einem Wert von 0 und Description als Passed anzeigt , wurden keine Probleme mit dem Laufwerk gefunden.
Wenn SMART Predict Failure Check FALSE mit einem anderen Wert als 0 anzeigt , suchen Sie in der folgenden Tabelle nach der Nummer für die ID , um herauszufinden, was dies bedeutet.(ID)
Bekannte (Known)ATA S . M. _ A. _ RT-Attribute (ID-Codes):(R.T. attributes (ID codes):)
Laufwerke unterstützen nicht alle Attributcodes (ID). Einige Codes sind spezifisch für bestimmte Laufwerkstypen (Magnetplatte, Flash, SSD ). Antriebe können unterschiedliche Codes für denselben Parameter verwenden.
Wenn für ein Laufwerk ein kritischer Status gemeldet wird, wird empfohlen, das Laufwerk sofort zu sichern und auszutauschen.
Read Error Rate
Throughput Performance
Spin-Up Time
Start/Stop Count
Reallocated Sectors Count
bad sectors
Read Channel Margin
Seek Error Rate
Seek Time Performance
Power-On Hours
Spin Retry Count
Recalibration Retries
Calibration Retry Count
Power Cycle Count
Soft Read Error Rate
Current Helium Level
Available Reserved Space
SSD Program Fail Count
SSD Erase Fail Count
SSD Wear Leveling Count
Unexpected Power Loss Count
Power Loss Protection Failure
- Bytes 0-1: Letztes Testergebnis als Mikrosekunden zum Entladen der Kappe, gesättigt bei maximalem Wert. Erwartetes Testergebnis(Test) im Bereich 25 <= Ergebnis <= 5000000, niedriger gibt spezifischen Fehlercode an.
- Bytes 2-3: Minuten seit dem letzten Test, Sättigung bei maximalem Wert.
- Bytes 4-5: Lebenslange Anzahl von Tests, wird beim Ein- und Ausschalten nicht inkrementiert, sättigt bei maximalem Wert.
Der normalisierte Wert wird auf eins gesetzt, wenn der Test fehlschlägt, oder auf 11, wenn der Kondensator bei zu hoher Temperatur getestet wurde, andernfalls auf 100.
Erase Fail Count
Wear Range Delta
Used Reserved Block Count Total
Unused Reserved Block Count Total
Program Fail Count Total
Non-4K Aligned Access Count
Erase Fail Count
SATA Downshift Error Count
Runtime Bad Block
End-to-End error / IOEDC
Head Stability
Induced Op-Vibration Detection
Reported Uncorrectable Errors
Command Timeout
High Fly Writes
flying height
Temperature Difference
Airflow Temperature
G-sense Error Rate
Power-off Retract Count
Emergency Retract Cycle Count
Unsafe Shutdown Count
Load Cycle Count
Load/Unload Cycle Count
Advanced Power Management
Automatic acoustic management
Temperature
Temperature Celsius
Hardware ECC Recovered
Reallocation Event Count
Current Pending Sector Count
(Offline) Uncorrectable Sector Count
UltraDMA CRC Error Count
Multi-Zone Error Rate
Write Error Rate
Soft Read Error Rate
TA Counter Detected
Data Address Mark errors
TA Counter Increased
Run Out Cancel
Soft ECC Correction
Thermal Asperity Rate
Flying Height
Spin High Current
surge current
Spin Buzz
Offline Seek Performance
Vibration During Write
Vibration During Write
Shock During Write
Disk Shift
G-Sense Error Rate
Loaded Hours
Load/Unload Retry Count
Load Friction
Load/Unload Cycle Count
Load ‘In’-time
Torque Amplification Count
Power-Off Retract Cycle
GMR Head Amplitude
Drive Life Protection Status
Life Left
Temperature
Endurance Remaining
Available Reserved Space
Media Wearout Indicator
Power-On Hours
Average erase count AND Maximum Erase Count
Good Block Count AND System(Free) Block Count
Head Flying Hours
Transfer Error Rate’
Total LBAs Written
Total LBAs Read
Total LBAs Written Expanded
Total LBAs Read Expanded
NAND Writes (1GiB)
Read Error Retry Rate
Minimum Spares Remaining
Newly Added Bad Flash Block
Free Fall Protection
Die obige Tabelle wurde von Microsoft bezogen .
Das waren die 3 Möglichkeiten, den SMART Failure Predict Status von Laufwerken in Windows 11/10 zu überprüfen !
How to check SMART Failure Predict Status of drives on Windows 11/10
S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) often written as SMART is a monitoring system included in computer hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and eMMC drives.
Its primary function is to detect and report various indicators of drive reliability with the intent of anticipating imminent hardware failures. In this post, we will show you how to check SMART Failure Predict Status of drives in Command Prompt, PowerShell, and Performance Monitor.
Check SMART Failure Predict Status of Drives in Windows 11/10
You must be signed in as an administrator to use this option.
If a hard drive (HDD) is currently in a turned-off state after being idle, it will not show up in this report. Only drives currently turned on and running will show up in this report.
1] To check SMART Failure Predict Status of Drives in Command Prompt, do the following:

- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type cmd and then hit Enter to open Command Prompt.
- In the command prompt window, type the command below and press Enter.
wmic /namespace:\\root\wmi path MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictStatus
- If the PredictFailure of a drive shows as FALSE, then no issues were found with the drive.
- If the PredictFailure of a drive shows as TRUE, then look up the Reason number for the ID in the table at the end of this post for what it means.
2] To check SMART Failure Predict Status of Drives in PowerShell, do the following:

- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Then press i on the keyboard to launch PowerShell.
- In the PowerShell console, type in or copy and paste the command below and hit Enter.
Get-WmiObject -namespace root\wmi -class MSStorageDriver_FailurePredictStatus
- If the PredictFailure of a drive shows as FALSE, then no issues were found with the drive.
- If the PredictFailure of a drive shows as TRUE, then look up the Reason number for the ID in the table at the end of this post for what it means.
Related: SMART Failure Predicted on Hard Disk error.
3] To check SMART Failure Predict Status of Drives in Performance Monitor, do the following:

- Invoke the Run dialog box.
- In the dialog box, type
perfmon and hit Enter to open Performance Monitor. - Expand Data Collector Sets, expand System in the left pane of Performance Monitor.
- Right-click or press and hold on System Diagnostics, and click/tap on Start.
This report will now start collecting data for 60 seconds. It may take up to an additional 60 seconds for the report to be generated.
- When the System Diagnostics report has finished generating, expand Reports > System > System Diagnostics in the left pane of Performance Monitor.
- Under System Diagnostics, click/tap on a report that was created (collected) on this date and time, and expand Disk Checks in the Basic System Checks section under Warnings.
If SMART Predict Failure Check shows FALSE with a value of 0 and Description shows as Passed, then no issues were found with the drive.
If SMART Predict Failure Check shows FALSE with a value other than 0, then look up the number for the ID in the table below for what it means.
Known ATA S.M.A.R.T. attributes (ID codes):
Drives do not support all attribute codes (ID). Some codes are specific to particular drive types (magnetic platter, flash, SSD). Drives may use different codes for the same parameter.
If a drive is reported to have a critical status, it is recommended to back up and replace the drive immediately.
IDAttribute nameDescription
0No issues found.
01
0x01
Read Error Rate
(Vendor specific raw value.) Stores data related to the rate of hardware read errors that occurred when reading data from a disk surface. The raw value has different structure for different vendors and is often not meaningful as a decimal number.
02
0x02
Throughput Performance
Overall (general) throughput performance of a hard disk drive. If the value of this attribute is decreasing there is a high probability that there is a problem with the disk.
03
0x03
Spin-Up Time
Average time of spindle spin up (from zero RPM to fully operational [milliseconds]).
04
0x04
Start/Stop Count
A tally of spindle start/stop cycles. The spindle turns on, and hence the count is increased, both when the hard disk is turned on after having before been turned entirely off (disconnected from power source) and when the hard disk returns from having previously been put to sleep mode.
05
0x05
Reallocated Sectors Count
Count of reallocated sectors. The raw value represents a count of the
bad sectors
that have been found and remapped. Thus, the higher the attribute value, the more sectors the drive has had to reallocate. This value is primarily used as a metric of the life expectancy of the drive; a drive which has had any reallocations at all is significantly more likely to fail in the immediate months.
06
0x06
Read Channel Margin
Margin of a channel while reading data. The function of this attribute is not specified.
07
0x07
Seek Error Rate
(Vendor specific raw value.) Rate of seek errors of the magnetic heads. If there is a partial failure in the mechanical positioning system, then seek errors will arise. Such a failure may be due to numerous factors, such as damage to a servo, or thermal widening of the hard disk. The raw value has different structure for different vendors and is often not meaningful as a decimal number.
08
0x08
Seek Time Performance
Average performance of seek operations of the magnetic heads. If this attribute is decreasing, it is a sign of problems in the mechanical subsystem.
09
0x09
Power-On Hours
Count of hours in power-on state. The raw value of this attribute shows total count of hours (or minutes, or seconds, depending on manufacturer) in power-on state. “By default, the total expected lifetime of a hard disk in perfect condition is defined as 5 years (running every day and night on all days). This is equal to 1825 days in 24/7 mode or 43800 hours.”
On some pre-2005 drives, this raw value may advance erratically and/or “wrap around” (reset to zero periodically).
10
0x0A
Spin Retry Count
Count of retry of spin start attempts. This attribute stores a total count of the spin start attempts to reach the fully operational speed (under the condition that the first attempt was unsuccessful). An increase of this attribute value is a sign of problems in the hard disk mechanical subsystem.
11
0x0B
Recalibration Retries
or
Calibration Retry Count
This attribute indicates the count that recalibration was requested (under the condition that the first attempt was unsuccessful). An increase of this attribute value is a sign of problems in the hard disk mechanical subsystem.
12
0x0C
Power Cycle Count
This attribute indicates the count of full hard disk power on/off cycles.
13
0x0D
Soft Read Error Rate
Uncorrected read errors reported to the operating system.
22
0x16
Current Helium Level
Specific to He8 drives from HGST. This value measures the helium inside of the drive specific to this manufacturer. It is a pre-fail attribute that trips once the drive detects that the internal environment is out of specification.
170
0xAA
Available Reserved Space
See attribute E8.
171
0xAB
SSD Program Fail Count
(Kingston) The total number of flash program operation failures since the drive was deployed. Identical to attribute 181.
172
0xAC
SSD Erase Fail Count
(Kingston) Counts the number of flash erase failures. This attribute returns the total number of Flash erase operation failures since the drive was deployed. This attribute is identical to attribute 182.
173
0xAD
SSD Wear Leveling Count
Counts the maximum worst erase count on any block.
174
0xAE
Unexpected Power Loss Count
Also known as “Power-off Retract Count” per conventional HDD terminology. Raw value reports the number of unclean shutdowns, cumulative over the life of an SSD, where an “unclean shutdown” is the removal of power without STANDBY IMMEDIATE as the last command (regardless of PLI activity using capacitor power). Normalized value is always 100.
175
0xAF
Power Loss Protection Failure
- Bytes 0-1: Last test result as microseconds to discharge cap, saturates at max value. Test result expected in range 25 <= result <= 5000000, lower indicates specific error code.
- Bytes 2-3: Minutes since last test, saturates at max value.
- Bytes 4-5: Lifetime number of tests, not incremented on power cycle, saturates at max value.
Normalized value is set to one on test failure or 11 if the capacitor has been tested in an excessive temperature condition, otherwise 100.
176
0xB0
Erase Fail Count
S.M.A.R.T. parameter indicates a number of flash erase command failures.
177
0xB1
Wear Range Delta
Delta between most-worn and least-worn Flash blocks. It describes how good/bad the wearleveling of the SSD works on a more technical way.
179
0xB3
Used Reserved Block Count Total
“Pre-Fail” attribute used at least in Samsung devices.
180
0xB4
Unused Reserved Block Count Total
“Pre-Fail” attribute used at least in HP devices.
181
0xB5
Program Fail Count Total
or
Non-4K Aligned Access Count
Total number of Flash program operation failures since the drive was deployed.
Number of user data accesses (both reads and writes) where LBAs are not 4 KiB aligned (LBA % 8 != 0) or where size is not modulus 4 KiB (block count != 8), assuming logical block size (LBS) = 512 B.
182
0xB6
Erase Fail Count
“Pre-Fail” Attribute used at least in Samsung devices.
183
0xB7
SATA Downshift Error Count
or
Runtime Bad Block
Western Digital, Samsung or Seagate attribute: Either the number of downshifts of link speed (e.g. from 6Gbit/s to 3Gbit/s) or the total number of data blocks with detected, uncorrectable errors encountered during normal operation. Although degradation of this parameter can be an indicator of drive aging and/or potential electromechanical problems, it does not directly indicate imminent drive failure.
184
0xB8
End-to-End error / IOEDC
This attribute is a part of Hewlett-Packard’s SMART IV technology, as well as part of other vendors’ IO Error Detection and Correction schemas, and it contains a count of parity errors which occur in the data path to the media via the drive’s cache RAM.
185
0xB9
Head Stability
Western Digital attribute.
186
0xBA
Induced Op-Vibration Detection
Western Digital attribute.
187
0xBB
Reported Uncorrectable Errors
The count of errors that could not be recovered using hardware ECC (see attribute 195).
188
0xBC
Command Timeout
The count of aborted operations due to HDD timeout. Normally this attribute value should be equal to zero.
189
0xBD
High Fly Writes
HDD manufacturers implement a
flying height
sensor that attempts to provide additional protections for write operations by detecting when a recording head is flying outside its normal operating range. If an unsafe fly height condition is encountered, the write process is stopped, and the information is rewritten or reallocated to a safe region of the hard drive. This attribute indicates the count of these errors detected over the lifetime of the drive.This feature is implemented in most modern Seagate drives and some of Western Digital’s drives, beginning with the WD Enterprise WDE18300 and WDE9180 Ultra2 SCSI hard drives, and will be included on all future WD Enterprise products.
190
0xBE
Temperature Difference
or
Airflow Temperature
Value is equal to (100-temp. °C), allowing manufacturer to set a minimum threshold which corresponds to a maximum temperature. This also follows the convention of 100 being a best-case value and lower values being undesirable. However, some older drives may instead report raw Temperature (identical to 0xC2) or Temperature minus 50 here.
191
0xBF
G-sense Error Rate
The count of errors resulting from externally induced shock and vibration.
192
0xC0
Power-off Retract Count
,
Emergency Retract Cycle Count
(Fujitsu), or
Unsafe Shutdown Count
Number of power-off or emergency retract cycles.
193
0xC1
Load Cycle Count
or
Load/Unload Cycle Count
(Fujitsu)Count of load/unload cycles into head landing zone position. Some drives use 225 (0xE1) for Load Cycle Count instead.Western Digital rates their VelociRaptor drives for 600,000 load/unload cycles, and WD Green drives for 300,000 cycles; the latter ones are designed to unload heads often to conserve power. On the other hand, the WD3000GLFS (a desktop drive) is specified for only 50,000 load/unload cycles.
Some laptop drives and “green power” desktop drives are programmed to unload the heads whenever there has not been any activity for a short period, to save power. Operating systems often access the file system a few times a minute in the background, causing 100 or more load cycles per hour if the heads unload: the load cycle rating may be exceeded in less than a year. There are programs for most operating systems that disable the
Advanced Power Management
(APM) and
Automatic acoustic management
(AAM) features causing frequent load cycles.
194
0xC2
Temperature
or
Temperature Celsius
Indicates the device temperature, if the appropriate sensor is fitted. Lowest byte of the raw value contains the exact temperature value (Celsius degrees).
195
0xC3
Hardware ECC Recovered
(Vendor-specific raw value.) The raw value has different structure for different vendors and is often not meaningful as a decimal number.
196
0xC4
Reallocation Event Count
Count of remap operations. The raw value of this attribute shows the total count of attempts to transfer data from reallocated sectors to a spare area. Both successful and unsuccessful attempts are counted.
197
0xC5
Current Pending Sector Count
Count of “unstable” sectors (waiting to be remapped, because of unrecoverable read errors). If an unstable sector is subsequently read successfully, the sector is remapped and this value is decreased. Read errors on a sector will not remap the sector immediately (since the correct value cannot be read and so the value to remap is not known, and also it might become readable later); instead, the drive firmware remembers that the sector needs to be remapped, and will remap it the next time it’s written. However, some drives will not immediately remap such sectors when written; instead the drive will first attempt to write to the problem sector and if the write operation is successful then the sector will be marked good (in this case, the “Reallocation Event Count” (0xC4) will not be increased). This is a serious shortcoming, for if such a drive contains marginal sectors that consistently fail only after some time has passed following a successful write operation, then the drive will never remap these problem sectors.
198
0xC6
(Offline) Uncorrectable Sector Count
The total count of uncorrectable errors when reading/writing a sector. A rise in the value of this attribute indicates defects of the disk surface and/or problems in the mechanical subsystem.
199
0xC7
UltraDMA CRC Error Count
The count of errors in data transfer via the interface cable as determined by ICRC (Interface Cyclic Redundancy Check).
200
0xC8
Multi-Zone Error Rate
The count of errors found when writing a sector. The higher the value, the worse the disk’s mechanical condition is.
200
0xC8
Write Error Rate
(Fujitsu)The total count of errors when writing a sector.
201
0xC9
Soft Read Error Rate
or
TA Counter Detected
Count indicates the number of uncorrectable software read errors.
202
0xCA
Data Address Mark errors
or
TA Counter Increased
Count of Data Address Mark errors (or vendor-specific).
203
0xCB
Run Out Cancel
The number of errors caused by incorrect checksum during the error correction.
204
0xCC
Soft ECC Correction
Count of errors corrected by the internal error correction software.
205
0xCD
Thermal Asperity Rate
Count of errors due to high temperature.
206
0xCE
Flying Height
Height of heads above the disk surface. If too low, head crash is more likely; if too high, read/write errors are more likely.
207
0xCF
Spin High Current
Amount of
surge current
used to spin up the drive.
208
0xD0
Spin Buzz
Count of buzz routines needed to spin up the drive due to insufficient power.
209
0xD1
Offline Seek Performance
Drive’s seek performance during its internal tests.
210
0xD2
Vibration During Write
Found in Maxtor 6B200M0 200GB and Maxtor 2R015H1 15GB disks.
211
0xD3
Vibration During Write
A recording of a vibration encountered during write operations.
212
0xD4
Shock During Write
A recording of shock encountered during write operations.
220
0xDC
Disk Shift
Distance the disk has shifted relative to the spindle (usually due to shock or temperature). Unit of measure is unknown.
221
0xDD
G-Sense Error Rate
The count of errors resulting from externally induced shock and vibration.
222
0xDE
Loaded Hours
Time spent operating under data load (movement of magnetic head armature).
223
0xDF
Load/Unload Retry Count
Count of times head changes position.
224
0xE0
Load Friction
Resistance caused by friction in mechanical parts while operating.
225
0xE1
Load/Unload Cycle Count
Total count of load cycles Some drives use 193 (0xC1) for Load Cycle Count instead. See Description for 193 for significance of this number.
226
0xE2
Load ‘In’-time
Total time of loading on the magnetic heads actuator (time not spent in parking area).
227
0xE3
Torque Amplification Count
Count of attempts to compensate for platter speed variations.
228
0xE4
Power-Off Retract Cycle
The number of power-off cycles which are counted whenever there is a “retract event” and the heads are loaded off of the media such as when the machine is powered down, put to sleep, or is idle.
230
0xE6
GMR Head Amplitude
(magnetic HDDs),
Drive Life Protection Status
(SSDs)Amplitude of “thrashing” (repetitive head moving motions between operations). In solid-state drives, indicates whether usage trajectory is outpacing the expected life curve
231
0xE7
Life Left
(SSDs) or
Temperature
Indicates the approximate SSD life left, in terms of program/erase cycles or available reserved blocks. A normalized value of 100 represents a new drive, with a threshold value at 10 indicating a need for replacement. A value of 0 may mean that the drive is operating in read-only mode to allow data recovery. Previously (pre-2010) occasionally used for Drive Temperature (more typically reported at 0xC2).
232
0xE8
Endurance Remaining
or
Available Reserved Space
Number of physical erase cycles completed on the SSD as a percentage of the maximum physical erase cycles the drive is designed to endure.Intel SSDs report the available reserved space as a percentage of the initial reserved space.
233
0xE9
Media Wearout Indicator
(SSDs) or
Power-On Hours
Intel SSDs report a normalized value from 100, a new drive, to a minimum of 1. It decreases while the NAND erase cycles increase from 0 to the maximum-rated cycles.Previously (pre-2010) occasionally used for Power-On Hours (more typically reported in 0x09).
234
0xEA
Average erase count AND Maximum Erase Count
Decoded as: byte 0-1-2 = average erase count (big endian) and byte 3-4-5 = max erase count (big endian).
235
0xEB
Good Block Count AND System(Free) Block Count
Decoded as: byte 0-1-2 = good block count (big endian) and byte 3-4 = system (free) block count.
240
0xF0
Head Flying Hours
or ‘
Transfer Error Rate’
(Fujitsu)Time spent during the positioning of the drive heads. Some Fujitsu drives report the count of link resets during a data transfer.
241
0xF1
Total LBAs Written
Total count of LBAs written.
242
0xF2
Total LBAs Read
Total count of LBAs read.
Some S.M.A.R.T. utilities will report a negative number for the raw value since in reality it has 48 bits rather than 32.
243
0xF3
Total LBAs Written Expanded
The upper 5 bytes of the 12-byte total number of LBAs written to the device. The lower 7 byte value is located at attribute 0xF1.
244
0xF4
Total LBAs Read Expanded
The upper 5 bytes of the 12-byte total number of LBAs read from the device. The lower 7 byte value is located at attribute 0xF2.
249
0xF9
NAND Writes (1GiB)
Total NAND Writes. Raw value reports the number of writes to NAND in 1 GB increments.
250
0xFA
Read Error Retry Rate
Count of errors while reading from a disk.
251
0xFB
Minimum Spares Remaining
The Minimum Spares Remaining attribute indicates the number of remaining spare blocks as a percentage of the total number of spare blocks available.
252
0xFC
Newly Added Bad Flash Block
The Newly Added Bad Flash Block attribute indicates the total number of bad flash blocks the drive detected since it was first initialized in manufacturing.
254
0xFE
Free Fall Protection
Count of “Free Fall Events” detected.
The above table has been sourced from Microsoft.
That’s it on the 3 ways to check SMART Failure Predict Status of drives in Windows 11/10!



